5 Workflow Problems AI Solves in Metal Production
- Steph Locke
- Blog
- January 13, 2026
Table of Contents
AI is transforming metal production by addressing five key workflow challenges that slow down operations and increase costs. Here’s how it helps:
- Reduces unplanned downtime: Predictive maintenance systems monitor equipment in real-time, catching issues before they lead to costly breakdowns.
- Improves quality control: AI detects defects with precision, outperforming manual inspections and minimising waste.
- Optimises production processes: Advanced data analysis identifies inefficiencies, boosting productivity and reducing energy use.
- Streamlines inventory management: AI offers accurate demand forecasting and material tracking, cutting waste and improving stock control.
- Simplifies compliance: Automated platforms handle documentation, saving time and reducing errors.
The result? Lower costs, fewer disruptions, and better efficiency for manufacturers. As 70% of manufacturers already use AI, and 82% plan to invest more, it’s clear that this technology is becoming indispensable in the industry.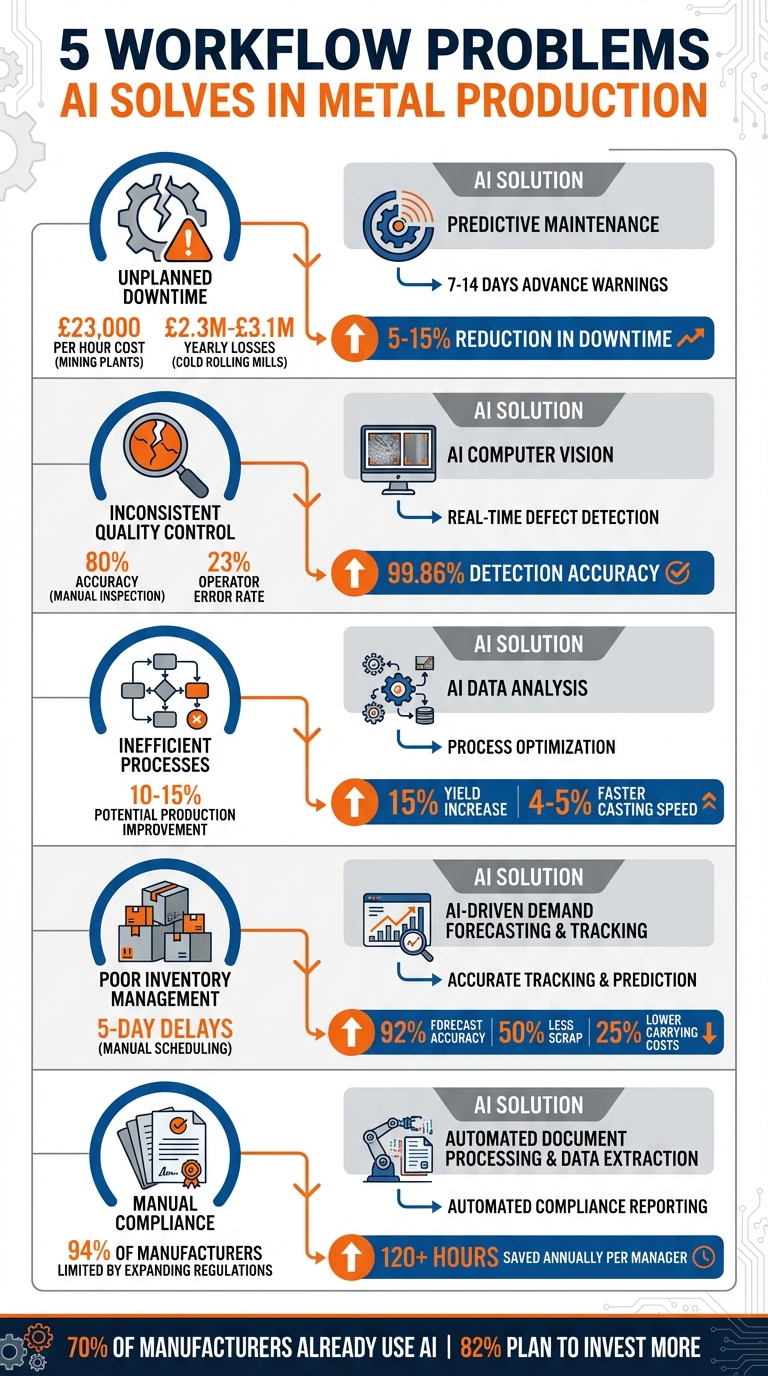
5 Workflow Problems AI Solves in Metal Production
Unplanned Downtime from Equipment Failures
In metal production, equipment failures can bring operations to a grinding halt. A breakdown in a rolling mill or blast furnace doesn’t just pause production - it can jeopardise worker safety, disrupt delivery schedules, and lead to massive financial losses. For example, unplanned downtime in a mining plant’s wet grinding process can cost around £23,000 per hour. In cold rolling mills, frequent failures might result in yearly losses ranging from £2.3 million to £3.1 million [4][5].
The environment in metal production facilities is unforgiving. Extreme heat, dust, vibrations, and contaminants accelerate the wear and tear on machinery [4]. Critical assets such as blast furnaces and rolling mills typically lack backup systems, meaning a single failure can shut down the entire operation [4]. Common issues include roller wear or misalignment in casting segments, motor and hydraulic breakdowns in pendulum shears, and pump or fan failures in cooling systems [4][7].
Traditional maintenance approaches struggle to keep up. Fixed-interval preventive maintenance often leads to over-servicing equipment that’s still functional or missing potential breakdowns because it doesn’t account for the machine’s actual condition [8]. Maintenance teams, already stretched thin, might miss early warning signs when manually analysing SCADA data [4]. By the time a problem becomes noticeable, it’s often too late to prevent costly shutdowns. Spotting these early indicators is crucial to avoiding expensive disruptions, but traditional methods fall short, calling for a more proactive approach.
AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance
AI is changing the game by turning maintenance into a proactive, data-driven process. Instead of reacting to failures or relying on arbitrary schedules, AI-powered systems use IoT sensors to monitor factors like vibration, temperature, pressure, acoustics, and lubrication continuously [9]. By analysing both historical and real-time data, these systems identify subtle patterns or deviations that hint at an impending failure - often issuing warnings 7 to 14 days in advance [7].
Take, for instance, a steel casting line that, in November 2020, implemented Falkonry’s Operational AI to monitor 150 sensors tracking roller forces, piston pressures, and casting speeds. The system detected warning patterns 7 to 10 days before segment roller failures, enabling the team to schedule maintenance during planned downtime and prevent production interruptions [7]. Similarly, a global steel manufacturer using Augury’s production health platform saved €1.76 million, reduced blast emissions by 3.5%, and increased blast furnace productivity by 2% on a single production line [6].
AI systems go beyond just flagging issues. They provide insights into the root cause - whether it’s bearing wear or misalignment - and recommend specific maintenance actions [6][7]. Chris Stanley, a Process Manager, shared how Augury’s AI platform identified cavitation in a pump in 2024:
“The alerts that we received on a pump caused us to investigate deeper and we found an operator had failed to open the discharge valve all the way, causing the cavitation. This saved 12 hours in downtime.” [6]
Gabriela Cadenas, SVP of Digital and Technology Americas at The Heineken Company, highlighted the broader impact of predictive maintenance:
“Predictive maintenance is one way AI is helping us improve our manufacturing… we do it when it’s actually needed, which, of course, increases and elevates the productivity of the line.” [8]
The benefits are clear: predictive maintenance can reduce facility downtime by 5–15% and boost labour productivity by 5–20% [9]. For metal producers, where margins are tight, these gains directly impact profitability and ensure more reliable delivery schedules for their customers.
Inconsistent Quality Control and Defect Detection
In industries where equipment reliability is critical, ensuring consistent quality is just as important.
Detecting defects in metal production is no easy task. Traditional visual inspections, which remain the cornerstone of quality control in many facilities, often miss internal flaws like porosity, inclusions, or deep cracks that can compromise structural integrity [11]. Even seemingly minor surface imperfections - like small cracks or cosmetic blemishes - can weaken components, leading to costly downgrades or customer rejections. The challenge is compounded by the speed of production lines, which can operate at thousands of metres per minute, far outpacing what manual checks can handle [12].
Human inspectors face limitations, too. Fatigue, inconsistent lighting, and repetitive tasks reduce manual inspection accuracy to around 80%, with operator errors accounting for about 23% of inaccuracies [15]. When thousands of components are inspected during a single shift, even a small error rate can quickly escalate. In cold rolling mills, for instance, undetected defects can result in production losses valued between £2.3 million and £3.1 million annually [5].
Traditional quality control systems also fall short. They rely on fixed thresholds and struggle to adapt to changing conditions, such as variations in lighting or complex surface textures [12]. Additionally, manual root cause analysis - often involving offline reviews of SCADA data across multiple parameters - delays detection, allowing defective materials to move further down the production line and increasing costs [5].
Real-Time Defect Detection with AI
AI is revolutionising quality control, offering real-time solutions to ensure product integrity and minimise defects.
AI-powered computer vision has brought a new level of precision and speed to quality control processes. Using advanced tools like Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) paired with ultrasonic, X-ray, and thermal sensors, AI systems can identify even the smallest defects - such as cracks, scratches, or inclusions - that are invisible to the human eye. These systems provide a detailed view of both surface and internal flaws [11][12][15].
The results speak for themselves. In 2023, researchers Sarvesh Sundaram and Abe Zeid from Northeastern University developed a custom CNN for inspecting casting products. Their system achieved an astounding defect detection accuracy of 99.86%, far exceeding the typical 80% accuracy of manual inspections [15]. This level of precision significantly reduces waste and rework.
One of AI’s standout features is its ability to act in real time. Instead of identifying defects during offline reviews hours or even days later, AI systems provide immediate feedback. This allows operators to isolate problematic materials before they progress further down the production line [12]. Some systems even go a step further, adjusting production parameters - like temperature or speed - on the fly when they detect conditions that could lead to defects [11].
The benefits are already evident in real-world applications. Audi AG, for example, uses an AI platform to inspect 1.5 million spot welds on 300 vehicles per shift. This ensures every weld is examined in real time, eliminating the need for statistical sampling [16]. Similarly, Ford Motor Company has deployed AI systems across more than 700 stations at its Dearborn Truck Plant to detect component misalignments and assembly defects as they occur [16]. Brandon Tolsma, Vision Engineer at Ford MTDC, highlighted the importance of this capability:
“As the vehicle goes through the assembly line, it gets harder and harder to access some of these components. I can’t stress enough how the real-time results are key in saving us time.” [16]
AI platforms also streamline compliance by linking inspection results to specific production batches, creating automated audit trails. For metal producers, these advancements not only provide immediate cost savings but also deliver long-term advantages. Studies show that adopting AI in steelmaking can reduce overall costs by 10–15%, with half of manufacturers reporting direct cost savings [10][16].
Inefficient Process Optimisation and Bottlenecks
After advancements in quality control, the next big hurdle for metal manufacturers is improving production processes. A key challenge lies in identifying production bottlenecks and uncovering their root causes.
Traditional methods for tracking efficiency often rely on manual data reviews and spreadsheet analysis. These approaches struggle to capture the full complexity of production, especially when multiple parameters interact across various stages. Bottlenecks often remain hidden until delays or waste become too obvious to ignore, and investigating these issues manually can be a time-consuming process.
The cost of these inefficiencies is hard to overlook. Studies suggest that fine-tuning existing equipment can improve production by 10–15% [20]. For instance, in February 2020, a large open-pit copper mine used machine learning to identify seven ore types instead of just three. By adjusting processing parameters in near real-time, the mine increased production by over 10% in just six months [20].
Energy consumption is another area where inefficiencies quietly add up. Without real-time optimisation, plants often operate with excessive temperature buffers or inefficient settings. Take the case of a zinc smelter in September 2023: AI analysis revealed that operators were maintaining a large temperature buffer in the fumer process. By refining process control, the plant reduced its average operating temperature by 22°C, leading to a noticeable improvement in metal recovery [20]. AI’s ability to analyse large data sets in real-time is now making it possible to uncover such inefficiencies more effectively than ever before.
AI for Production Data Analysis
AI is transforming process optimisation by tackling inefficiencies head-on. Machine learning platforms integrate with existing PLCs and SCADA systems, pulling real-time data from sensors that measure variables like temperature, pressure, and machine speed.
Rather than replacing skilled metallurgists and engineers, these systems act as decision-support tools. They process vast amounts of complex data and highlight specific areas that may need attention. Dr Petra Krahwinkler, Senior Expert for AI at Primetals Technologies, explains:
“By deploying AI’s vast data processing capabilities, we can analyse more - and much more complex - data from across the plant than a human ever could” [19].
The impact of these tools is both measurable and fast. For example, in November 2021, a US steel manufacturer used an AI-based data lake to connect end-to-end process data for a specific product family. Within just eight weeks, the machine learning model pinpointed parameters that boosted product yield by 15% and reduced variability, creating approximately £410,000 in annual value for a single product line [21]. Similarly, in 2025, JSW Steel’s Dolvi Works plant implemented the ABB Ability Smart Melt Shop solution. The results were impressive: a 4–5% increase in casting speed, an additional 24,000 tonnes of annual output, and a £205,000 reduction in energy costs [18].
AI scheduling agents take things even further by analysing millions of variables to determine the best production order. These systems not only maximise profit but also ensure timely delivery. They’ve demonstrated reductions in yield loss by as much as 20–40% [17]. Tarun Mathur, Global Portfolio Manager for Digital Solutions at ABB Process Industries, highlights the importance of preparation:
“The first step on this journey is ensuring data readiness. Whilst many producers generate vast data streams, they often lack the infrastructure to make this data actionable” [18].
Poor Material Handling and Inventory Management
Inventory management issues continue to plague metal manufacturers, often disrupting production and efficiency.
One of the biggest challenges lies in controlling inventory and tracking materials. Many companies still rely on manual systems, such as spreadsheets and disconnected data sources, forcing managers to scramble for accurate, real-time stock information across multiple sites. This issue, often referred to as “data retrieval challenges” within the industry, creates a ripple effect of inefficiencies [14].
The lack of clear inventory visibility comes with serious consequences. Traditional forecasting methods, which often rely on simple averages, can result in either surplus inventory or stock shortages. On top of that, manual scheduling through spreadsheets can delay critical decisions by as much as five days [24][23]. Without proper material tracking, these inefficiencies lead to lower production yields and an increase in scrap rates [14].
Financially, the stakes are high. High-value metals demand precise stock management, but fluctuating demand and unpredictable lead times make manual tracking prone to errors [22]. To prevent production halts, companies often turn to costly “just-in-case” inventory strategies, which increase warehousing and carrying expenses [24]. As Josh Bartel, CEO and Co-founder of Hydrian, explains:
“Lead time forecasting is every bit as important as demand forecasting, and it can be just as difficult” [24].
Material traceability adds another layer of complexity. Ensuring that the correct materials are used - by linking mill certificates and heat codes to inventory records - is critical. However, many companies still rely on paper-based systems, forcing managers to manually verify material lineage [14]. Overcoming these hurdles requires more advanced approaches that move beyond manual processes.
AI-Driven Inventory Optimisation
AI is transforming inventory management in the metals industry, just as it has in other areas like maintenance and production. With AI-powered systems, tracking and predictive analytics are automated, eliminating the need for manual intervention. Machine learning algorithms evaluate factors like consumption rates, lead times, and safety stock levels to determine the best reorder points [22]. These systems also account for external influences - such as seasonal trends, economic shifts, and market conditions - rather than relying solely on historical data [22].
The impact is clear. For example, in 2021, BBQGUYS partnered with Hydrian to implement AI-driven predictive forecasting. By incorporating customer demand patterns and weather data, they reduced distressed inventory to just 0.6% of their purchases. Dan Hauser, Senior Director of Operations at BBQGUYS, highlighted this success:
“Only 0.6% of our purchases has gone into a distressed state” [24].
Similarly, a major steel company achieved over 92% accuracy in demand forecasting by consolidating 15 separate data sources through AI. This also cut production planning time by an impressive 98% [23].
AI scheduling tools take optimisation further by evaluating a wide range of variables to create the most efficient production plans. These tools factor in supply variations, machine availability, and changeover costs - challenges that overwhelm traditional manual methods [17]. For instance, Midland Steel worked with GoSmarter to implement AI-driven production planning for cutting long products. By analysing open orders against available stock, they reduced scrap rates by 50% [14].
Automation also simplifies material traceability. Systems can digitise mill certificates and link them directly to inventory records, ensuring complete traceability from supplier to customer [14]. This not only saves production managers over 120 hours annually but also improves compliance accuracy [14]. Additionally, AI-based inventory management has been shown to reduce carrying costs by up to 25% [25], while predictive algorithms identify potential inventory imbalances and supplier risks before they disrupt production [3].
Manual Compliance and Documentation Delays
Compliance documentation has long been a stumbling block for manufacturers, creating delays that disrupt production schedules and drive up costs. Managers often find themselves sifting through multiple web portals, overflowing inboxes, and stacks of paper records to locate certificates [13][14]. This time-consuming process pulls employees away from production tasks, further compounding inefficiencies.
The manual handling of documents - renaming PDFs, inputting data into spreadsheets or ERPs, and breaking down bulk certificates - adds another layer of complexity. Not only does this waste valuable time, but it also risks data errors. Inaccurate data entry can lead to traceability issues, increasing the likelihood of material misuse and compliance failures [26][13][14][1]. When documentation is scattered, ensuring that tasks like welding are carried out with the correct, compliant materials becomes a significant challenge [14].
The growing complexity of regulatory requirements only adds to the burden. In one survey, 94% of manufacturers reported that expanding regulations were limiting their ability to invest in workforce development, equipment upgrades, and facility improvements [27]. Despite these challenges, many companies still rely on outdated manuals and repetitive training sessions to manage compliance [13].
AI-driven solutions are stepping in to address these inefficiencies, streamlining document handling and data integration.
Automating Compliance with AI Platforms
AI platforms are transforming compliance processes by digitising mill certificates and instantly extracting critical technical details, such as chemical compositions and mechanical properties [14][26].
In June 2025, Cardiff-based tech company Nightingale HQ introduced the “MillCert Reader” on its GoSmarter platform. This tool automates data extraction and document renaming in mere seconds [26][28]. As Nightingale HQ described:
“MillCert Reader… saves hours every month by automatically pulling key data from mill certificates. It can rename documents in seconds which is a task that is usually painfully manual” [26].
The time savings are impressive. For instance, automating the conversion of bulk mill certificates into single-page PDFs for specific heat codes saved one production manager over 120 hours annually [14]. By eliminating the need to manually search through piles of documents, these tools create smoother workflows and free up compliance managers to focus on higher-value tasks [13].
These platforms don’t just save time - they also improve traceability. By linking material data directly to inventory records, they ensure that tasks like welding are carried out with the right materials. This integration provides a clear product history for customers, reducing the risk of misusing materials in critical operations [14].
The adoption of AI in compliance is gaining momentum. While 70% of manufacturers report using AI to enhance efficiency [2], there is still plenty of room for further adoption. Tony Woods, CEO of Midland Steel, highlighted the broader benefits:
“The integration of AI and digital tracking has significantly improved our operational efficiency and sustainability performance” [13].
Conclusion
AI is revolutionising the metal production industry by addressing five major workflow challenges. By leveraging predictive maintenance, manufacturers can reduce unexpected downtime through early fault detection. Real-time defect detection ensures consistent product quality, while production data analysis helps optimise energy consumption and scheduling. Additionally, inventory optimisation accurately forecasts material demand to reduce waste, and automated compliance platforms simplify document handling.
The results speak for themselves. Companies implementing AI have reported impressive gains, including 30% shorter cycle times and 25% better resource utilisation [29]. Many have also seen improvements in their sustainability efforts. This targeted approach tackles inefficiencies head-on, as evidenced by the fact that 70% of manufacturers are already using AI, with 82% planning to increase their investment in the technology [2].
The secret to success lies in starting small and focusing on high-impact areas. Instead of attempting a full-scale overhaul, manufacturers should address specific challenges - whether it’s predictive maintenance, quality control, or compliance documentation. Platforms like GoSmarter make this easier with transparent, usage-based pricing and quick-start options [13].
Transitioning from manual to data-driven processes not only enhances operational efficiency but also strengthens competitiveness in an industry facing challenges like supply chain disruptions, rising energy costs, and workforce shortages. AI empowers manufacturers to tackle these issues while improving sustainability and overall performance.
For metals manufacturers looking to improve compliance and streamline production workflows, exploring AI-driven platforms designed for these tasks is a practical and effective starting point. Embracing these focused AI strategies is no longer optional - it’s essential to stay competitive in today’s ever-changing market.
FAQs
How does AI help reduce downtime in metal production?
AI-driven predictive maintenance is transforming metal production by cutting down equipment downtime. Using real-time data from sensors installed on machinery like rolling mills, furnaces, and material-handling systems, AI keeps a close watch on factors such as vibration, temperature, and power consumption. This allows it to spot early signs of wear or irregularities, enabling maintenance teams to address potential problems during planned downtime instead of scrambling to fix unexpected breakdowns.
This forward-thinking approach minimises unplanned stoppages, boosts equipment performance, and keeps workflows running smoothly. For manufacturers in the UK, the benefits are clear: fewer lost shifts, reduced overtime expenses, and better alignment with sustainability targets. GoSmarter’s AI platform takes this a step further by automating data collection and delivering actionable insights, helping teams save valuable time while maintaining steady production levels.
How does AI enhance quality control and detect defects in metal production?
AI is reshaping quality control in metal production by bringing real-time precision to defect detection. Through advanced machine learning, it analyses sensor data and images to spot problems like surface cracks, inclusions, or dimensional irregularities - issues that might be too subtle for the human eye to catch. And the best part? This happens instantly during production, cutting down on waste and rework while maintaining consistent quality standards.
But AI doesn’t stop at visual checks. It also keeps a close eye on critical process parameters like temperature, pressure, and feed rates. By predicting when a product might drift out of specification, it gives operators the chance to make adjustments on the fly, ensuring production stays within strict tolerances. For manufacturers using tools like GoSmarter, AI even takes over time-consuming tasks like analysing mill certificates and inspection data. This means teams can focus their energy on solving challenges instead of getting bogged down in paperwork.
How does AI improve inventory management in metal manufacturing?
AI has revolutionised inventory management, shifting it from a manual, reactive process to a smart, data-driven approach. By analysing real-time data from sources like sensors, ERP systems, and mill certificates, AI delivers a precise picture of stock levels and material flow. Machine learning takes it a step further by studying historical usage patterns, production schedules, and lead times to predict demand. This means manufacturers can fine-tune reorder points, cut down on safety stock, and avoid the pitfalls of overstocking or running out of materials.
GoSmarter’s AI-powered platform makes this process even easier. It automates data collection from PDFs, spreadsheets, and IoT devices, ensuring inventory data is always current. The platform forecasts material needs, sends timely alerts for replenishment, and aligns inventory with production plans. This not only reduces waste and holding costs but also helps metal manufacturers in the UK build a more efficient and responsive supply chain.