How AI Optimises Steel Production Processes
- Ruth Kearney
- Blog , Learning
- January 8, 2026
Table of Contents
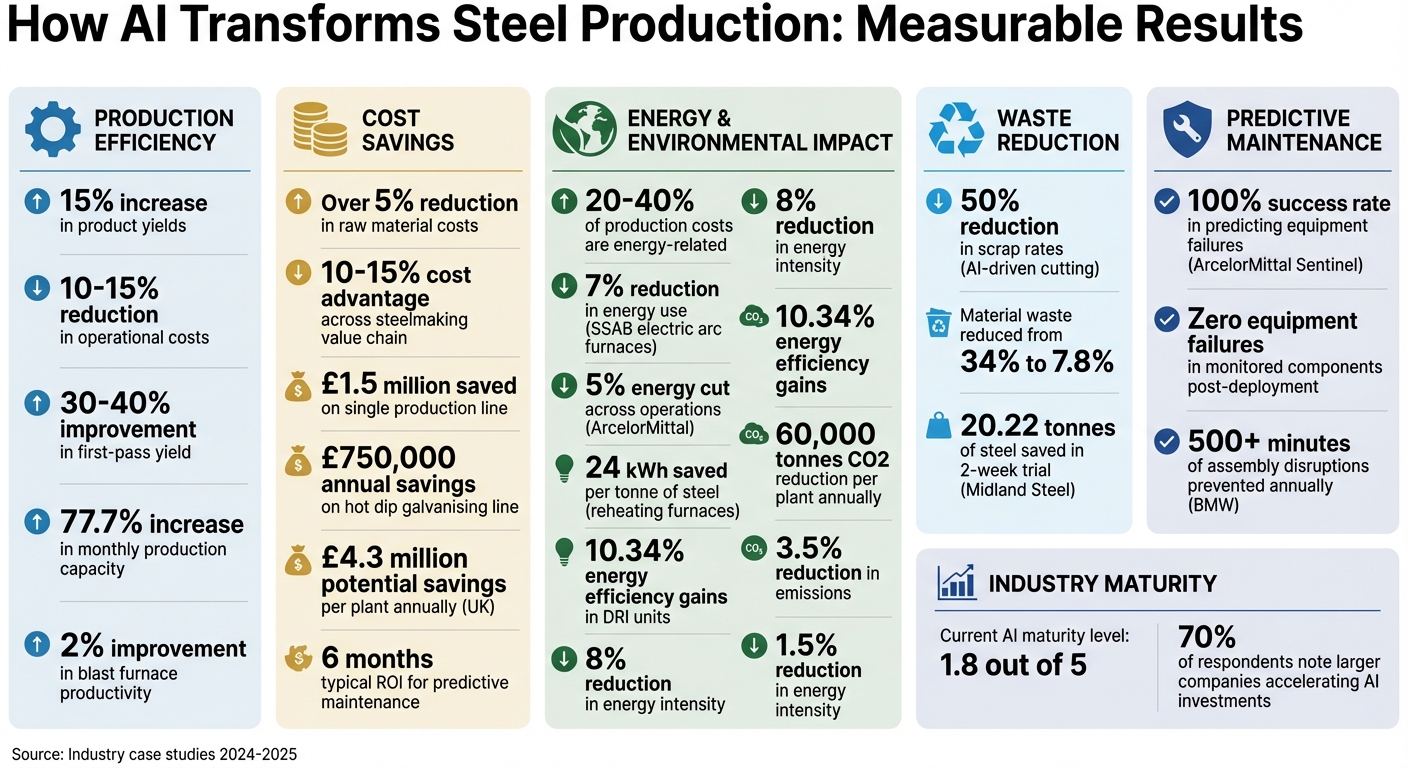
AI is transforming steel production by reducing waste, cutting costs, and improving efficiency. By analysing real-time data, AI can optimise furnace temperatures, raw material usage, and production schedules, delivering measurable results. For example, companies using AI have achieved:
- 15% increase in product yields: Reducing material waste and boosting profits.
- 10–15% reduction in operational costs: Through predictive maintenance and energy savings.
- Lower CO₂ emissions: Optimising processes to cut energy use and waste.
AI-powered tools, like predictive maintenance systems and real-time quality control, help manufacturers avoid equipment failures and detect defects instantly. This shift from reactive to proactive management ensures smoother operations and better resource use. For steelmakers, adopting AI is key to staying competitive, meeting regulations, and improving productivity.
AI Impact on Steel Production: Key Performance Metrics and Cost Savings
Real-Time Process Monitoring and Quality Control
AI for Real-Time Monitoring
Traditional sampling methods often result in delays when it comes to detecting defects. AI has transformed this process by analysing data as production occurs, allowing operators to identify and address issues instantly.
IoT sensors play a key role here, gathering data from critical areas like blast furnaces, rolling mills, and cooling systems. These sensors track essential parameters such as temperature, pressure, chemical composition, and vibrations at every stage of production.
Take the example of Worthington Steel’s Delta, Ohio facility. Since 2018, they’ve incorporated real-time monitoring into their reliability strategy, using a combination of vibration and oil analysis. By May 2025, this predictive maintenance programme had expanded to 17 sites [9]. Their system processes triaxial vibration data to detect issues like imbalance, misalignment, and bearing wear. At the same time, it monitors motor current signals to identify problems in driven systems [6]. High-speed control solutions like Hitachi’s HITSODAS operate on timescales as short as tens of milliseconds, ensuring consistent strip thickness and flatness in flat steel products [6]. Dr. Petra Krahwinkler, Senior Expert for AI at Primetals Technologies, highlights this capability:
The advantage of AI is that it can do this analysis in real-time [5].
These advancements not only ensure production quality but also enhance cost efficiency and operational reliability. The seamless integration of data also sets the stage for automated quality checks in subsequent production stages.
Automating Quality Control with AI
Real-time monitoring paves the way for advanced automated quality control, powered by cutting-edge computer vision systems. These systems, equipped with high-resolution cameras, continuously observe production lines, detecting surface defects, cracks, and even hidden impurities [11]. In iron ore pelletising, for instance, AI-powered vision systems evaluate the size and shape of pellets on the go, enabling operators to make immediate adjustments rather than discovering flaws hours later [5].
The benefits of AI-driven computer vision go beyond defect detection. By analysing production variables in real time, these systems can predict potential failures, improving first-pass yield by 30–40% [10]. A practical example comes from BMW Group, which in October 2025 implemented an AI-supported system to monitor conveyor technology during vehicle assembly. This innovation prevented over 500 minutes of assembly disruptions annually [10].
Another success story involves a long-product metal producer collaborating with Wizata to optimise its continuous casting process. By deploying 76 AI models, the company predicted failures in four cutting torches. Operators received real-time SMS and email alerts, allowing them to avoid unplanned downtime and hit all key performance indicators from the outset [12].
This shift from reactive to proactive quality control eliminates the costly cycle of discovering defects after production is complete. It not only reduces waste but also ensures consistent product quality across every batch while supporting the streamlined production practices discussed earlier.
Predictive Maintenance to Reduce Downtime
Using AI to Predict Equipment Failures
Machine learning is transforming how industries approach equipment maintenance. By analysing sensor data from critical assets like blast furnaces, rolling mills, cooling systems, and conveyor motors, AI can detect early warning signs of potential failures. Sensors monitor key metrics such as vibration patterns, temperature shifts, pressure variations, and motor currents. This data is then compared with historical performance baselines, allowing AI models to flag irregularities for further investigation by maintenance teams [14][6]. This approach not only complements real-time monitoring but also extends its benefits to improving equipment reliability.
For example, specialised clamp sensors can identify subtle changes in current that hint at wear and tear in gearboxes or downstream machinery [6]. Instead of waiting for a motor to seize or a hydraulic actuator to fail, AI systems catch these anomalies before they escalate into expensive breakdowns [14][6]. This early detection strategy paves the way for significant operational and financial advantages.
In 2024, ArcelorMittal introduced its in-house AI platform, “Sentinel”, to predict failures in motors and hydraulic systems. During pilot programmes at plants in Canada and northern France, the platform successfully forecasted every potential issue. Since its full-scale deployment, including at mills in Brazil, the company has reported zero equipment failures in monitored components [4]. Carlos Alba, Head of AI and Digital R&D at ArcelorMittal, highlighted:
All the potential failures have been predicted, meaning the maintenance teams can come in and fix them before they go wrong. You’re shifting from a situation of relatively frequent failures to one where reliability is getting close to 100% [4].
Cost and Efficiency Gains from Predictive Maintenance
The financial and operational benefits of predictive maintenance are hard to ignore. By preventing equipment failures, AI enhances uptime and reduces costs. Traditional maintenance methods often involve expensive emergency repairs or routine servicing that may not align with the actual condition of the equipment [14]. In contrast, AI-driven maintenance offers a cost advantage of 10–15% in steel production [2].
Consider this: one steel manufacturer improved blast furnace productivity by 2% and cut emissions by 3.5%, translating to savings of roughly £1.5 million on a single production line. They also reduced energy intensity by 1.5% [13]. In another case, implementing AI for maintenance and production scheduling on a hot dip galvanising line saved nearly £750,000 annually [4].
Beyond direct cost savings, predictive maintenance optimises how resources are allocated. Maintenance teams can prioritise genuine risks instead of wasting time on routine checks or emergency fixes. Ensuring equipment operates within ideal conditions also boosts throughput, improves product yield, and extends the lifespan of machinery [13][14]. Many companies see a return on their investment in predictive maintenance technology within just six months [13].
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Compliance
AI for Energy Usage Optimisation
Energy expenses make up a hefty 20% to 40% of total production costs in steel manufacturing, making it critical to find ways to cut down on waste and improve efficiency [18]. This is where AI steps in, using operational data to identify inefficiencies and automatically fine-tune processes to lower energy consumption.
One powerful tool in this space is the digital twin, which acts as a virtual replica of manufacturing operations. These digital models allow AI to simulate various operating conditions and pinpoint the most efficient settings - without the need for costly physical changes [8]. Tarun Mathur, Global Digital Lead for Metals at ABB, describes their function:
AI-enabled process digital twins act as an autopilot for production…you can run it in an energy efficient mode or a productivity mode, and it automatically optimises the parameters [17] - link no longer works.
This kind of optimisation doesn’t just save money - it also brings environmental benefits.
Take predictive temperature modelling for reheating furnaces, for example. In November 2025, software startup Deep.Meta collaborated with Spartan UK’s Gateshead plate mill to trial the “Deep.Optimiser.” Using 40 years of production data alongside real-time furnace sensors, the AI tool could predict the exact moment steel reached the ideal rolling temperature. The result? Energy savings of 24 kWh per tonne of steel [7]. Osas Omoigiade, Founder of Deep.Meta, pointed out:
Many steel producers waste energy by not fully utilising interdependent production data [7].
Other applications include Direct Reduction Iron (DRI) units, where machine learning adjusts cooling gas and burner flows in real-time. This has led to 10.34% energy efficiency gains, with projected annual electricity savings of around 21,900,000 kWh [15]. Swedish manufacturer SSAB saw a 7% reduction in energy use for its electric arc furnaces, while ArcelorMittal achieved a 5% energy cut across its operations [18].
By improving energy efficiency, manufacturers can reduce both costs and environmental impact - a win-win scenario.
Reducing Environmental Impact with AI
AI isn’t just about saving money; it’s also a game-changer for reducing emissions. By optimising energy use, steel manufacturers can cut carbon emissions while staying ahead of increasingly strict environmental regulations. For example, deep learning models have been shown to lower energy intensity by up to 8% and carbon emissions by 20% in heavy industry plants [8].
A case in point: Midland Steel. In early 2025, the company used Nightingale HQ’s GoSmarter.ai platform during a two-week trial to optimise rebar cutting. Their AI-powered “Rebar Optimisation Tool” analysed real-time inventory and order data to minimise waste. Over 193 jobs, the tool processed 734 tonnes of steel, saving 20.22 tonnes of material and significantly reducing embodied energy and CO2 emissions [3]. Tony Woods, Founder & CEO of Midland Steel, commented:
This collaboration has delivered concrete results, proving that smart technology can have a direct, measurable impact on reducing carbon emissions in steel manufacturing [3].
The potential global impact is staggering. Rebar waste accounts for 3–5% of total steel production, contributing 17–28.3 million tonnes of CO2 emissions annually [3]. AI-driven efficiency in steel plants could save £4.3 million in costs and cut 60,000 tonnes of CO2 emissions per plant each year [8].
Beyond tackling energy waste, AI also helps manufacturers meet regulatory demands like the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) and the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) [3]. It even reduces harmful pollutants such as fine particulate matter, sulphur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides by optimising fuel use [5]. Dr. Petra Krahwinkler, Senior Expert for AI at Primetals Technologies, summed it up perfectly:
We want to deploy just the right amount of heat and raw materials to achieve the required level of quality at the lowest cost and with the least amount of waste [5].
Production Scheduling and Inventory Management
Optimising Production Schedules with AI
Steel manufacturing production schedules are a complex balancing act. Factors like equipment constraints, material availability, delivery deadlines, and energy costs all need to align seamlessly. Traditional methods often falter under this complexity, causing bottlenecks and inefficiencies. This is where AI steps in, using Machine Learning Constraint Programming (MLCP) to replicate the decision-making expertise of seasoned planners. By considering all variables, these systems create schedules that are both efficient and practical [6].
One standout approach involves bio-inspired algorithms. ArcelorMittal, for instance, developed ant algorithms to streamline production sequencing. Carlos Alba, Head of AI and Digital R&D at ArcelorMittal, explained:
We took inspiration from nature and developed bio-mimicking algorithms based on ants looking for food… They take the optimal path – a straight line – and this can be mathematically modelled for the production process. [4]
This innovation has been transformative. On a single hot dip galvanising line, it delivered savings of about £1 million annually. When scaled to entire steel shops, the cost benefits grew significantly [4].
AI also enables real-time heat scheduling, which matches production demand with energy availability. By aligning energy-intensive processes with greener energy supplies, this approach not only cuts operating costs but also lowers CO₂ emissions [16]. For example, Spartan UK’s Gateshead plate mill introduced the Deep.Optimiser AI tool in 2024. Using 40 years of production data and live furnace sensor readings, the system pinpointed the perfect moment to remove steel for rolling. This resulted in a potential 20% boost in productivity [7].
The benefits don’t stop there. AI-driven solutions have reduced material waste from 34% to just 7.8%. When paired with digital twin-driven smelting management, monthly production capacity has seen a remarkable 77.7% increase [19]. Across the steelmaking value chain, these advancements can cut overall costs by 10–15% [2]. Beyond improving efficiency, these systems pave the way for real-time inventory integration, creating a more connected and responsive production process.
Inventory Management and Supply Chain Integration
While AI enhances production scheduling, it also revolutionises inventory management, ensuring a steady and high-quality supply of raw materials. Traditional methods, like spreadsheet-based tracking, are prone to errors and delays - especially in complex supply chains involving multiple suppliers and diverse material specifications. AI eliminates these issues by automating stock monitoring, order tracking, and supplier management in real time. It even integrates mill and material certificates directly into inventory systems [20]. This ensures that the right materials are used for the right tasks, such as matching specific steel compositions to welding requirements [20].
In early 2025, Midland Steel teamed up with GoSmarter to implement an AI-driven production planner for cutting long products. By factoring in open orders and available stock, the system created more efficient cutting plans, slashing scrap rates by 50% [20]. Tony Woods, Founder & CEO of Midland Steel, highlighted the impact:
The integration of AI and digital tracking has significantly improved our operational efficiency and sustainability performance. [3]
AI doesn’t just track inventory - it also optimises raw material mixes and predicts demand, reducing costs and preventing supply disruptions. These systems can lower input costs by over 5% while improving end-to-end product yields by more than 15% [1].
Implementing AI in Steel Manufacturing
Preparing for AI Adoption
For steel manufacturers looking to tap into the potential of AI, careful planning and preparation are essential. A strong data foundation is the first step. This means creating an end-to-end data lake that connects process data from raw material input to the final stages of production. Legacy systems will need to be upgraded to capture this comprehensive data. Tracking entire product families is also crucial, as it uncovers critical interactions between production variables [1].
Adopting AI isn’t just about technology - it requires a shift in mindset too. As BCG explains:
Many steel manufacturers haven’t yet embraced AI, but that doesn’t mean they can’t. All that’s required is an openness to experimentation and a willingness to change [1].
It’s important to note that manufacturers don’t need perfect data to begin. The focus should be on identifying areas with lower investment requirements but high potential returns. IT gaps can be addressed as the project progresses [1].
Phased AI Deployment
Rolling out AI in phases reduces risks and helps build momentum. Typically, this process unfolds in three stages:
- Phase 1 (Months 1–6): Start with pilot projects targeting a specific product family with reliable data. During this phase, AI operates in a supervised mode, offering recommendations while human teams make the final decisions. This builds trust in the system and highlights any data gaps [1]. For instance, one manufacturer managed to improve yield by 15% within just eight weeks, resulting in an annual value of £400,000 [1].
- Phase 2 (Months 6–24): Expand successful pilots by deploying AI models in high-impact areas like melting or milling. These early successes can help fund further upgrades to IT infrastructure [1].
- Phase 3 (Months 24+): Fully integrate AI into operational systems, such as SCADA, to enable real-time optimisation. Following this phased approach can lead to a 10–15% cost advantage, even though the steel industry’s current AI maturity level is rated at just 1.8 out of 5 [1][2].
Once the pilot projects demonstrate value, fully integrated AI systems can take operational efficiency to the next level.
Team Collaboration for Successful AI Integration
While technology is important, human collaboration is the key to unlocking AI’s potential in steel manufacturing. Effective integration requires teamwork across R&D, IT, management, and operational departments. Carlos Alba highlights the importance of combining expertise from these areas to scale AI successfully [4].
Take ArcelorMittal as an example. Their AI research team of around 100 people pairs junior researchers with experienced domain experts. This collaborative approach has allowed them to scale AI globally. One of their notable successes is the “Sentinel” predictive maintenance platform, which achieved a 100% success rate in predicting motor failures during its pilot phase [4].
Trust from shop floor operators is equally critical. At Spartan UK’s Gateshead plate mill, the Deep.Optimiser AI tool was developed with input from veteran staff. Dr Osas Omoigiade, Founder of Deep.Meta, shared:
One operator, who has been there for 30 years, told me that this tool made his job five times faster, reducing the risk of operator errors [7].
Using explainable AI - where operators can see and understand how decisions are made - further enhances trust and ensures smoother adoption [21]. When implemented thoughtfully, AI can deliver lower costs, improved efficiency, and compliance with environmental goals, as highlighted throughout this guide.
Conclusion
AI is reshaping steel production in ways that are hard to ignore. By reducing raw material costs by over 5% and increasing yield by more than 15%, it delivers a cost advantage of 10–15% [1][2]. In the UK alone, AI has the potential to save up to £4.3 million per plant while slashing CO₂ emissions by 60,000 tonnes [8].
These financial and environmental gains highlight a significant opportunity for an industry still in the early stages of its digital journey. With the sector’s AI maturity currently rated at just 1.8 out of 5 [2], there’s a clear gap - and a chance to innovate. As Akio Ito from Roland Berger puts it:
AI has a myriad of highly beneficial use cases across the steelmaking value chain and companies can readily exploit these if they focus on our AI boost priorities. [2]
The evidence is compelling. Many manufacturers have already seen tangible benefits from implementing AI in areas like production efficiency and resource optimisation.
Starting this transformation doesn’t require flawless data or enormous budgets. Small, focused pilot projects in high-impact areas can make a difference. Building trust through explainable AI and fostering collaboration between data experts and seasoned metallurgists can help ensure success. With 70% of industry respondents noting that larger companies are accelerating their AI investments [2], the competitive edge is shifting fast.
For steel manufacturers aiming to improve efficiency, meet environmental goals, and stay ahead of the curve, adopting AI is no longer just an option - it’s a necessity. The challenge now is to act swiftly and embrace the opportunities AI offers.
FAQs
How does AI help lower CO₂ emissions in steel production?
Artificial intelligence is transforming the steel industry by helping to slash CO₂ emissions through smarter, more efficient processes. Using tools like digital twins and real-time analytics, AI optimises key areas such as furnace operations, production schedules, and scrap management. These adjustments reduce energy use and waste, directly lowering carbon emissions.
With AI-driven technologies, steel plants have the potential to reduce emissions by as much as 60,000 tonnes of CO₂ annually. On top of that, better scrap management further cuts emissions tied to waste. The result? Not only does this align with sustainability targets, but it also boosts the overall efficiency of operations.
What are the benefits of using predictive maintenance in steel production?
Predictive maintenance is transforming the steel industry by leveraging AI to keep a close watch on equipment and anticipate potential breakdowns. This proactive approach drastically reduces unplanned downtime - some plants report cutting stoppages by up to 50%. It also extends machinery life and trims the need for maintaining large spare-parts inventories.
Another major advantage is improved operational efficiency. For example, blast furnace productivity can see a 2% increase, while energy use and material waste drop significantly. These improvements not only enhance production rates but also help lower carbon emissions, supporting sustainability objectives.
Tools like GoSmarter make this process even easier. By automating data collection, predicting maintenance needs, and embedding insights directly into workflows, these platforms save time, cut down on paperwork, and enable UK steel manufacturers to focus on fine-tuning their production processes.
How does AI enhance energy efficiency in steel production?
AI is reshaping the energy-heavy steel production process by using sensor data to make operations smarter and more efficient. It analyses inputs like temperature, power usage, and material flow in real time to fine-tune heating cycles in electric-arc or blast furnaces. This precision helps cut down on excess fuel use and avoids costly errors.
Additionally, AI can schedule production during times when electricity is cheaper or sourced from renewable energy, which not only lowers energy costs but also reduces carbon emissions. Tools like GoSmarter take it a step further by automating tasks such as inventory management and production planning. This allows manufacturers to cut waste, use less energy per tonne of steel, and save money - all while taking steps towards more sustainable practices.