
Top ERP Strategies for Supply Chain Risks
- Steph Locke
- Blog
- January 12, 2026
Table of Contents
Top ERP Strategies for Supply Chain Risks
Metals manufacturers in the UK are facing supply chain challenges due to geopolitical tensions, Brexit, and economic volatility. Modern ERP systems offer solutions by improving visibility, automating processes, and enabling better risk management. Key strategies include:
- Real-Time Inventory Management: Integrating IoT and AI for accurate stock tracking and demand forecasting.
- Supplier Risk Management: Centralised data for performance tracking and risk assessment across all supplier tiers.
- Predictive Analytics: Tools to forecast disruptions, model scenarios, and adjust operations proactively.
- Compliance Automation: Streamlined workflows to meet UK regulations and maintain audit readiness.
- Cross-Department Collaboration: Unified platforms for improved communication and decision-making.
ERP systems, combined with tools like GoSmarter, address specific industry needs, such as mill certificate digitisation and inventory optimisation, helping manufacturers streamline operations and respond effectively to disruptions.
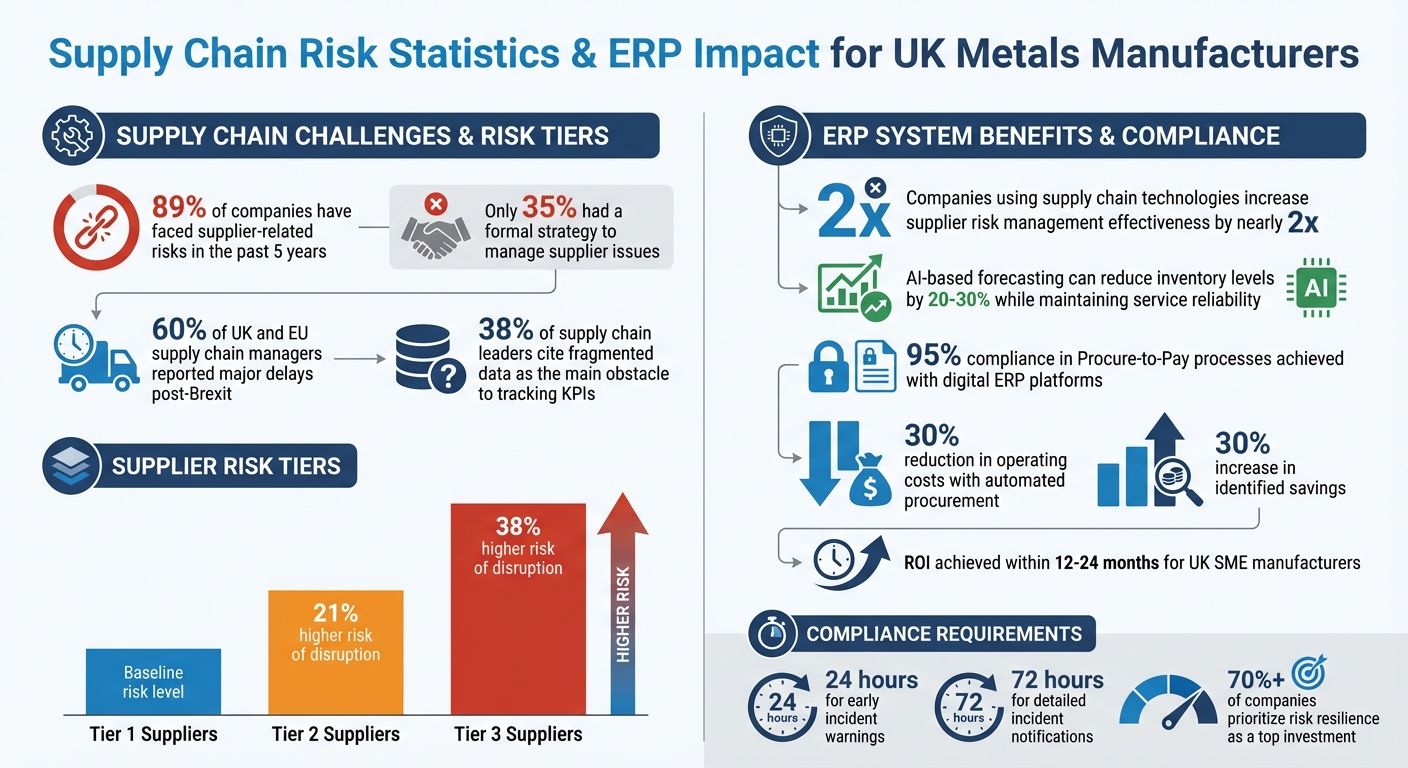
Supply Chain Risk Statistics and ERP Impact for UK Metals Manufacturers
Supply Chain Risk Statistics and ERP Impact for UK Metals Manufacturers
Real-Time Inventory Visibility and Control
ERP Inventory Management for Metals Manufacturing
Modern ERP systems bring together finance, procurement, and production data into a single, centralised hub. This eliminates the chaos of juggling disconnected spreadsheets or outdated records, ensuring everyone operates from the same, accurate information source [6][2].
By integrating with IoT sensors, RFID technology, and handheld scanning devices, these systems enable instant tracking of raw materials and finished goods. Mobile ERP applications synchronise this data in real time, offering a clear picture of physical stock at any given moment [1][10]. This capability is especially crucial for managing raw material batches, mill certificates, and scrap yields - key elements in reducing production risks within metals manufacturing [1][7].
“ERP systems empower businesses with real-time tracking and control of inventory levels, enabling more responsive and dynamic decision-making.” – GO-ERP [10]
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) modules further enhance efficiency by aligning material orders directly with production needs. This ensures timely and precise deliveries of metals, replacing the outdated practice of holding excessive buffer inventories. The result? Improved cash flow and a reduced risk of shortages during production runs. Additionally, this system supports advanced forecasting, enabling manufacturers to plan demand with greater precision.
Demand Forecasting and Automated Processes
With real-time data as a foundation, AI-powered forecasting tools within ERP systems analyse historical trends and market behaviour. This allows manufacturers to predict future demand far more accurately than traditional methods [8][9]. By identifying consumption patterns, these tools help avoid the pitfalls of slow-moving stock and the costly disruptions of stockouts.
Automated replenishment takes this a step further, generating purchase orders automatically when inventory reaches predefined minimum levels [2][10]. The system accounts for supplier lead times and production schedules, reducing manual errors and freeing up staff for more strategic tasks. For metals manufacturers navigating volatile market conditions, this blend of predictive analytics and automation offers a reliable way to maintain optimal inventory levels.
Supplier Risk Assessment and Management
ERP systems go beyond just managing inventory; they play a critical role in reducing supplier risks by centralising performance data and automating verification processes.
ERP Supplier Scorecards and Performance Tracking
With a centralised ERP platform, all supplier-related data - such as bids, orders, invoices, delays, and quality metrics - comes together in one place, making it easily accessible [2]. This consolidated approach allows manufacturers to create performance scorecards that evaluate suppliers based on crucial metrics like On-Time In-Full (OTIF) delivery rates, Parts Per Million (PPM) defect rates, and financial indicators such as debt-to-equity ratios [2][11].
The benefit of real-time tracking is clear: it helps identify supplier issues early, whether it’s a decline in delivery performance or financial instability. This early warning system enables manufacturers to act quickly, preventing disruptions before they impact production.
ERP systems equipped with advanced tools go even further by assessing risks beyond Tier 1 suppliers. Using AI-powered parsing and OCR technology, these systems can analyse historical contracts and bills of materials to identify vulnerabilities at Tier 2 and Tier 3 supplier levels, where risks are statistically higher. For example, Tier 2 suppliers face about 21% more risk of disruption than Tier 1, while Tier 3 suppliers carry a 38% higher risk [11].
A real-world example from September 2023 illustrates this: an automotive Tier 1 supplier used AI-powered tools to review contracts and audit data over two months. The analysis revealed that nearly all the metal parts in their product line relied on steel from a single upstream mill. This discovery led the company to adjust its sourcing strategy, reducing its reliance on a single supplier and mitigating potential vulnerabilities.
“Companies leveraging supply chain technologies and digital transformation in risk management increase their effectiveness in supplier risk tactics by nearly 2x.” – Gartner [4]
Insights like these seamlessly integrate into automated procurement processes, further reducing supplier risks.
Automated Procurement and Supplier Verification
Traditional supplier verification methods are often slow and prone to errors. ERP systems streamline this process by automating supplier onboarding and tracking procurement activities, significantly reducing the workload for procurement teams [2][12]. Automated workflows handle tasks such as verifying certificates of conformance, ensuring compliance with data privacy and ESG standards, and flagging underperforming suppliers.
Real-time digital dashboards and control towers provide instant alerts on critical developments, such as supplier insolvency, geopolitical events, or transport delays. This allows manufacturers to respond quickly and effectively [4][11]. For instance, a metals manufacturer used ERP-based predictive algorithms to anticipate a shortage of key alloy components by analysing raw material price trends. This foresight enabled them to stockpile materials and secure long-term contracts, shifting their approach from reactive problem-solving to proactive risk management.
In volatile markets, this ability to anticipate and address risks is vital for keeping operations running smoothly.
Predictive Analytics for Risk Forecasting
Predictive analytics is transforming risk management by shifting the focus from reacting to disruptions to preventing them. Instead of scrambling to fix problems after they occur, ERP systems equipped with advanced tools - like machine learning algorithms and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural networks - analyse both historical trends and real-time data to identify potential risks before they arise [13][14].
Consider this: 89% of companies have faced supplier-related risks in the past five years, yet only 35% had a formal strategy to manage such issues [4]. Predictive analytics helps bridge this gap by equipping manufacturers with the ability to anticipate disruptions. This forward-looking approach also enables advanced scenario modelling and more dynamic inventory management.
Scenario Modelling and Risk Planning
Building on predictive analytics, ERP systems allow manufacturers to simulate “what-if” scenarios to evaluate supply chain vulnerabilities. These simulations can model disruptions such as geopolitical events, transport delays, material shortages, or equipment failures, providing insights into their potential impact across operations [2][14].
For metals manufacturers, this capability is particularly useful for identifying risks beyond their immediate suppliers. For instance, advanced ERP tools can highlight hidden dependencies, such as multiple Tier 1 suppliers relying on the same steel mill. Data shows that Tier 2 suppliers face a 21% higher risk of disruption, while Tier 3 suppliers encounter a 38% higher risk compared to Tier 1 [11].
A global brewery serves as a compelling example. By using predictive analytics to forecast raw material trends, the company was able to stockpile supplies and secure long-term contracts, effectively avoiding a major disruption [11].
Adjusting Inventory Based on Market Trends
Predictive analytics also empowers manufacturers to fine-tune inventory levels based on market dynamics and demand fluctuations. Tools that focus on demand sensing leverage real-time data from IoT devices, market trends, and external factors to detect shifts as they happen. This enables preemptive adjustments to stock levels, which is critical given that 38% of supply chain leaders cite fragmented data as the main obstacle to tracking key performance indicators [14].
ERP systems combine internal data - like sales, inventory, and production capacity - with external influences such as weather patterns, market trends, and supplier performance. This integration creates a comprehensive view for accurate forecasting [2][15]. For metals manufacturers, who often face volatile raw material prices and fluctuating energy costs, these predictive models can flag potential shortages or price spikes. With this information, procurement strategies can be adjusted in advance, ensuring a more resilient supply chain.
“The catalyst for supply chain transformation is a unified data model, which integrates disparate sources into a single coherent view.” – Raj Jaasthi, Principal, Business Consulting, Ernst & Young LLP [14]
The rise of predictive analytics marks a significant shift in supply chain management. By focusing on strategic planning rather than reactive problem-solving, manufacturers can better navigate market uncertainty and build a more risk-aware supply chain.
Compliance and Audit Preparation
Keeping up with post-Brexit trade rules and the changing landscape of UK regulations can feel like a daunting task. However, ERP systems simplify this process by automatically tracking, documenting, and reporting every transaction. Instead of scrambling to meet compliance requirements, businesses can rely on these platforms to maintain structured records that align with HMRC and ISO 31000 standards. This proactive approach helps reduce risks that could otherwise disrupt supply chains.
The importance of compliance remains high. After Brexit, 60% of UK and EU supply chain managers reported major delays when moving goods into the UK, often due to incomplete paperwork [16]. For metals manufacturers managing intricate international supply chains, ERP systems can handle the creation of commercial invoices that meet all mandatory requirements, such as including EORI numbers, Tax ID numbers, net weights, and country of origin [16]. These automated processes also ensure adherence to strict UK regulatory and VAT standards.
Meeting UK Regulatory Requirements
ERP systems make compliance easier by automating workflows that adapt to regulatory updates. For example, when it comes to HMRC VAT rules, modern ERP platforms can process multi-currency transactions, account for daily exchange rate changes, and generate invoices with accurate payment terms and credit details [16].
The introduction of the UK Cybersecurity and Resilience Bill, similar to NIS 2, adds another layer of complexity for manufacturers operating in critical sectors. Under these new rules, businesses must notify regulators of significant incidents within 24 hours for early warnings and 72 hours for detailed notifications [18]. ERP systems help manage this requirement by offering real-time visibility into third-party dependencies and enabling quick incident reporting. Additionally, advanced modules can perform denied-party screening, automatically checking suppliers against international watchlists to ensure compliance with UK sanctions and trade restrictions [21].
“Risk management is no longer a back-office function – it’s now central to business strategy, with more than 70% of companies prioritising risk resilience as a top investment.” – KPMG [19]
Beyond regulatory compliance, ERP systems also play a vital role in safeguarding data integrity, which is crucial for audits.
Maintaining Audit Trails with ERP
Centralised ERP platforms record every transaction, inventory movement, and data modification with precise timestamps. This creates detailed audit trails that are essential for monitoring risks across the supply chain. By eliminating manual data entry errors, these systems provide tamper-proof documentation that regulatory inspectors can rely on [17][20]. When audits occur, businesses can quickly access historical data without the hassle of searching through paper files or fragmented systems.
The benefits go beyond simply passing inspections. In 2025, CACI adopted Ivalua’s Source-to-Pay platform to digitise procurement and accounts payable processes. By transitioning to nearly paperless operations and improving supplier collaboration, CACI achieved 95% compliance in Procure-to-Pay processes, reduced operating costs by 30%, and increased identified savings by 30% [19]. This example highlights how audit-ready systems not only meet regulatory demands but also enhance overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Cross-Department Collaboration and Risk Monitoring
Supply chain disruptions rarely stay confined to a single department. When a supplier misses a delivery deadline for raw materials, the ripple effects hit procurement, production schedules, finance, and logistics all at once. To address these challenges, effective collaboration across departments is essential, and ERP systems play a key role in making this possible. By integrating various risk management functions, ERP systems eliminate the silos that often hinder teamwork. Instead of each department relying on separate spreadsheets or databases, everyone works from a shared, centralised platform. This ensures that decisions are made using accurate, up-to-date information [2].
Centralised Data for Team Coordination
Modern ERP platforms bring together data from procurement, finance, engineering, and logistics into a single, unified system. For example, when the procurement team negotiates with a new supplier, the finance department can instantly review payment terms, while production teams can check delivery schedules and inventory levels. This level of integration is especially valuable for metals manufacturers, where aligning raw material needs from the shop floor with supply chain planning is critical [5].
The advantages of this coordination are clear. Companies that adopt supply chain technologies and digital tools for risk management see nearly double the effectiveness in handling supplier risks [4]. Real-time, role-specific dashboards ensure that each team member accesses data relevant to their function. Andy Coussins, Head of International at Epicor, highlights the value of this approach:
“Visualisation solutions keep supply chains moving by bringing data to life, giving manufacturers access to insights in context, specifically for the function they’re tasked with” [3].
This unified data strategy also enables continuous monitoring and agile team responses. With everyone working from the same “single source of truth”, manufacturers are better equipped to identify and address risks proactively.
Continuous Risk Monitoring and Staff Training
Real-time data from ERP systems allows manufacturers to shift from reacting to disruptions to proactively managing risks. Automated tools can flag potential issues - like supplier insolvency or geopolitical changes - and send alerts to the relevant teams [4][22]. This proactive approach is crucial, as 89% of companies have faced supplier risk events in the past five years, with nearly two-thirds struggling to respond promptly due to a lack of predictive frameworks [4].
While automation is a game-changer, the human element remains just as important. Comprehensive training ensures staff can fully utilise ERP systems and adapt to procedural changes that foster better cross-department collaboration [2][12]. Mark Jensen, Product Marketing Expert at Epicor, underscores this point:
“Using one system provides a single source of truth and makes it easier to train and onboard new employees” [1].
Regular reviews of supply chain performance metrics also help teams refine their risk management strategies, keeping the organisation prepared for emerging challenges [2][4].
Using GoSmarter for ERP-Enhanced Supply Chain Management
GoSmarter
Building on the ERP-driven risk management strategies mentioned earlier, GoSmarter offers tailored solutions specifically designed for metals manufacturers.
While ERP systems form the backbone of supply chain operations, metals manufacturers often encounter unique challenges that standard ERP setups can’t fully address. GoSmarter steps in to fill these gaps. Instead of replacing ERP systems, this AI-powered platform works alongside them, automating processes like mill certificate management and inventory optimisation - areas that frequently slow down operations.
Key Features of GoSmarter for Metals Manufacturers
One of the standout features of GoSmarter is its ability to tackle mill certificate digitisation, a notoriously time-intensive process. For example, a single import can contain up to 71 pages of documentation, leading to delays when handled manually [16]. GoSmarter automates data extraction from these certificates, ensuring that raw material details are accurately captured and linked to production batches for complete traceability [25][26]. This level of precision is crucial for industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical manufacturing, where every step must meet strict regulatory requirements.
AI-driven inventory management is another game-changer. It builds on ERP stock tracking by using predictive analytics to identify slow-moving inventory and set optimal replenishment points. Studies show that AI-based forecasting can reduce inventory levels by 20–30% while maintaining service reliability [26]. The platform also provides real-time insights through live dashboards and smart rules for invetory picking [24][25]. This eliminates the reliance on static spreadsheets, which often lead to errors and chaos as businesses scale.
These features not only complement ERP systems but also pave the way for more effective pricing strategies.
GoSmarter Pricing Plans
GoSmarter offers flexible pricing options to suit manufacturers of all sizes:
| Product | Best For | Key Capabilities | Pricing (Annual) | Pricing (Monthly) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GoSmarter Insights | Anyone wanting quick insight | - Scrap weight and cost calculation - Carbon emissions estimation - Free insight tools | Free | Free |
| Product Lineage | Compliance & traceability | - AI scanning of mill & material certificates - Automatic linking of inventory to heat codes - Retrieve mill certificate PDFs by heat code | £275 / month | £350 / month |
| Business Manager | Inventory & order control | - Customer & supplier management - Inventory tracking - Order management - Scrap tracking | £400 / month | £500 / month |
| Production Planner | Production planning teams | - Long product cutting planning - Integrates with inventory and orders - First-draft cutting plans | POA | POA |
Conclusion
For UK metals manufacturers, supply chain disruptions have become an expected part of doing business. As highlighted earlier [4], the real challenge lies not in avoiding these disruptions but in being prepared to tackle them effectively. Strategies like real-time inventory monitoring, thorough supplier risk evaluation, predictive analytics, compliance management, and fostering collaboration across departments are key to building a supply chain that can withstand these hurdles.
Integrated systems are crucial in this context. They break down data silos, enabling quicker and more informed decision-making when issues arise. However, metals manufacturers face specific challenges that standard ERP systems often struggle to handle, such as managing mill certificates, ensuring batch traceability, and meeting material-specific compliance requirements.
This is where tools like GoSmarter make a difference. By complementing traditional ERP systems, GoSmarter automates time-consuming tasks and strengthens traceability processes essential to metals manufacturing. Tasks like managing compliance documentation and maintaining audit trails, which often bog down operations, are streamlined. Research shows that companies adopting digital transformation and supply chain technologies can nearly double the effectiveness of their supplier risk management strategies [4]. This shift from reactive to proactive risk management transforms operational efficiency.
Proactive risk management requires a robust ERP system paired with specialised automation tools. Such integration creates a unified data environment, simplifying training, speeding up onboarding, and providing the agility needed to handle challenges like Brexit delays, geopolitical tensions, and market fluctuations.
Interestingly, most UK SME manufacturers see a return on investment from cloud ERP systems within 12 to 24 months [28]. By enhancing ERP systems with targeted solutions, metals manufacturers can not only adapt to regulatory and market challenges but also achieve ROI faster, allowing them to focus on strategic priorities that drive growth.
FAQs
How do ERP systems help metals manufacturers manage supplier risks effectively?
ERP systems give metals manufacturers a centralised, real-time view of supplier data, making risk management more effective. By bringing together details like purchase orders, delivery performance, quality checks, and financial health, these systems eliminate isolated data and enable continuous tracking of supplier reliability and compliance.
With advanced analytics, ERP platforms can evaluate suppliers based on key risk factors - such as credit ratings, mill certificate validity, or defect rates - and send automatic alerts if problems arise. This proactive method allows procurement teams to tackle potential disruptions before they escalate. On top of that, scenario modelling tools let manufacturers simulate the effects of losing a supplier and plan alternative sourcing strategies, which strengthens supply chain resilience.
For the metals industry, ERP systems tailored to their needs can automate essential tasks like managing mill certificates, monitoring raw material inventory in tonnes, and ensuring compliance with regulations. Solutions like GoSmarter’s AI-powered platform simplify these processes, ensuring risk-related data stays accurate and accessible. This empowers manufacturers to make well-informed decisions and maintain a strong, compliant supply chain.
How can predictive analytics help mitigate supply chain risks?
Predictive analytics is an essential tool for spotting and addressing potential supply chain hiccups before they escalate. By examining both historical and real-time data, it can predict risks like delays, inventory shortages, or supplier setbacks. This allows businesses to act in advance, reducing the potential impact on their operations.
When combined with an ERP system, predictive analytics takes decision-making to the next level. It can simulate what-if scenarios and recommend solutions, such as tweaking inventory levels or exploring alternative suppliers. Take GoSmarter’s AI-powered platform as an example - it supports metals manufacturers by predicting challenges, fine-tuning production schedules, and ensuring operational efficiency. The result? A supply chain that’s resilient and better prepared for unexpected changes.
How does GoSmarter enhance ERP systems for metals manufacturers?
GoSmarter works hand-in-hand with traditional ERP systems to tackle the specific needs of the metals manufacturing sector. While ERP platforms handle core operations like finance, production, and inventory management, GoSmarter steps in to automate specialised tasks. This includes managing mill certificates, tracking raw alloy stock, and ensuring adherence to industry regulations. The result? Less paperwork and more time for teams to concentrate on strategic priorities.
By integrating with ERP systems, GoSmarter uses existing data to boost supply chain resilience and enhance efficiency. It evaluates production schedules, flags potential issues, fine-tunes inventory levels, and automatically generates compliance documents. This combination allows manufacturers to make quicker, data-backed decisions, all while keeping processes aligned with the familiar £-based financial system used in the UK.