
AI in Steel Inventory: Case Studies and Results
- Steph Locke
- Blog , Case studies
- January 7, 2026
Table of Contents
AI is transforming steel inventory management, helping manufacturers solve long-standing issues like manual errors, stock imbalances, and inefficiencies. Here’s the takeaway:
- Problem: Steel manufacturers face costly challenges such as errors in manual stock counts, overstocking, stockouts, and logistical inefficiencies.
- Solution: AI systems automate tasks, improve accuracy, and provide real-time insights. Tools like predictive analytics, AI vision systems, and centralised operations have been game-changers.
- Results: Companies like Tata Steel and Norfolk Iron & Metal have reported significant savings, improved planning, and reduced downtime. For example, Tata Steel achieved £1.1 billion in EBITDA savings and a 1:10 ROI.
From AI-powered counting systems to predictive logistics, these technologies are reducing costs, increasing efficiency, and enhancing safety in steel manufacturing.
Case Study 1: AI-Powered Counting for Complex Metal Inventory
Challenge: Errors in Manual Counting
Steel manufacturers often struggle with accurately counting components like billets, beam blanks, and blooms. These items, typically stored outdoors, are exposed to harsh conditions that lead to rust, dust, and corrosion, making embossed serial numbers difficult to read. Manual counting in such environments is not only slow but also highly error-prone. Workers face tough warehouse conditions, including poor lighting, temperature swings, and the need to identify components that may be degraded. The challenge intensifies in high-volume production settings, especially with continuous casting - a process responsible for over 90% of global liquid steel production. This creates thousands of components that require precise tracking [8]. Clearly, a more reliable and efficient solution was needed.
Solution: AI Vision and Automation
In 2007, Zurich-based SMS Concast, under the leadership of CEO Stephan Feldhaus, joined forces with CSEM to create “Steeltrack.” This AI-driven vision system was specifically designed to tackle the challenges of metal inventory counting. By combining machine learning algorithms with tri-colour lighting, Steeltrack ensures high precision even in dusty conditions and fluctuating lighting environments. The system is trained to identify unique physical traits like shape contours, rhomboidity, and bulging patterns, enabling it to accurately count and recognise components - even when serial numbers are obscured or missing [8].
Results: Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
Steeltrack delivered an impressive 99.8% identification accuracy, even when dealing with incomplete or unreadable serial numbers [8]. Stephan Feldhaus praised the system’s performance:
CSEM has helped us develop a highly accurate tracking system for our customers that ensures the highest possible quality to their long steel products [8].
Case Study 2: Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimisation
Challenge: Overstocking and Stockouts
Steel manufacturers have always found it challenging to strike the right balance between holding too much inventory and running out of stock. Relying on manual, Excel-based planning proved inadequate for dealing with complex lead times and ever-changing market conditions [9][2]. This outdated approach led to two major problems: overstocking, which locked up valuable capital, and stockouts, which resulted in missed sales opportunities. The situation was made even more difficult by the need to predict demand across a variety of product lines, particularly when external factors - such as shifts in the agriculture and energy sectors - added further uncertainty.
Solution: AI-Driven Forecasting
To address these challenges, manufacturers turned to AI-powered predictive analytics. Norfolk Iron & Metal made a significant leap under the guidance of Ben Dubois, Director of Data Analytics. The company adopted the DataRobot AI platform, which allowed them to automate predictive analytics and move beyond simply analysing past data. By employing a multi-feature time-series regression model that incorporated external industry indicators, the platform produced much more accurate demand forecasts. DataRobot’s ability to integrate multiple data sources alongside time-series data played a key role in improving forecast reliability [3].
Similarly, Tata Steel began a major digital transformation in 2018, spearheaded by Chief Information Officer Jayanta Banerjee. The company centralised operations from five Indian plants into an Integrated Remote Operations Centre (iROC) and developed 260 algorithms to handle procurement, forecasting, and planning [7]. These AI systems, often referred to as “Digital Brains” by industry experts, synchronised demand and supply in real time, effectively replacing fragmented, homegrown solutions [9].
Results: Cost Reduction and Improved Planning
The results of these AI-driven strategies were both measurable and impactful. Norfolk Iron & Metal managed to avoid sales losses caused by stockouts while significantly cutting the costs associated with overstocking. The company also sped up the transition from raw data to actionable insights, reducing the time needed from weeks - or even months - to under an hour [3].
Tata Steel saw even more dramatic outcomes. By October 2023, the company reported £1.1 billion in EBITDA savings through its data and AI initiatives. Their return on investment jumped from a 1:4.3 ratio in 2018 to an impressive 1:10 ratio. As Banerjee put it:
Every dollar I spend, I get $10 back [7].
In another example, replacing manual Excel-based planning with AI-driven master planning improved on-time, in-full (OTIF) delivery rates while reducing excess inventory [9]. These advancements highlight the transformative potential of AI in tackling long-standing supply chain challenges.
Case Study 3: Predictive Logistics in Steel Manufacturing
This case study delves into how AI is reshaping logistics in steel production, building on earlier examples of its impact on inventory management.
Challenge: Inefficient Logistics and Delays
Steel manufacturers face a host of logistical challenges that disrupt inventory flow and drive up costs. Traditional scheduling methods, often reliant on a small group of experts, struggle to adapt quickly when faced with sudden order changes or equipment breakdowns [5]. Adding to the complexity, the extreme operating conditions - like conveyors running at temperatures as high as 1,500°C - render standard vibration sensors useless [1][10]. Andy Roegis, Industrial Digitalisation Manager for Northern Europe at ArcelorMittal, described the issue:
In the steel industry, assets frequently operate in conditions that are not hospitable to sensitive sensor technologies. The conveyors at our hot strip mill are a critical part of the production process, but it’s virtually impossible to use manual or vibration-based techniques to assess their condition [10].
Beyond equipment monitoring, outdated systems posed further challenges. Disconnected legacy software made it difficult to track individual parts across complex production stages [2]. Additionally, tasks like sampling and weighing in rolling lines were still performed manually, exposing workers to hazardous conditions [1]. These systemic inefficiencies called for a major shift in how logistics were managed.
Solution: AI-Powered Predictive Systems
To tackle these challenges, steel manufacturers turned to AI-driven solutions to overhaul logistics planning. At ArcelorMittal’s Ghent hot strip mill, the SAM4 AI-based condition monitoring system was introduced in September 2024. This system uses hardware installed in motor control cabinets to safely monitor electrical signals, predicting equipment failures months in advance [10].
Tata Steel took a different approach, centralising operations from five plants into an Integrated Remote Operations Centre (iROC) in 2018. They implemented 260 algorithms to optimise everything from procurement to shipping routes and logistics timing. As Banerjee explained:
AI is used a lot in decision making… questions such as which raw material to buy; when, where and what is the best route to ship it into the plant… are best answered by AI models [7].
In Wu’an City, twelve major steel enterprises adopted AI solutions in 2023, leveraging 5G networks and robotic automation. Tasks like slag removal and sampling were automated, with Xinxing Ductile Iron Pipes deploying tag welding robots to handle length calibration and metre-weight measurement [1]. These innovations enabled real-time monitoring, centralised decision-making, and automation of high-risk tasks.
Results: Faster Turnaround and Cost Savings
The results were game-changing. At ArcelorMittal’s Ghent facility, the SAM4 system detected 27 potential failures up to seven months in advance during its pilot phase, avoiding 31 hours of unplanned downtime and allowing maintenance to be scheduled at optimal times [10]. Tata Steel saw significant financial gains, reporting EBITDA savings of £1.1 billion and improving their return on investment from 1:4.3 to 1:10 [7].
In Wu’an, the collective efforts of steel enterprises led to annual savings of over ¥200 million, a 65.6% reduction in equipment downtime, and a 60% boost in labour efficiency [1]. Hazardous roles were drastically reduced, with the number of high-risk positions dropping from 23 to just 6 - a 74% decrease [1]. Liu Zhenggang highlighted the impact:
Particularly in rolling line weighing, the installation of tag welding robots and robotic sampling systems enables online automated sampling with automatic length calibration and metre-weight measurement. This innovation has boosted labour efficiency by 60% [1].
These advancements showcase how AI-driven predictive logistics can cut costs, enhance safety, and streamline operations across the steel manufacturing supply chain.
Comparison of AI Deployments in Steel Inventory
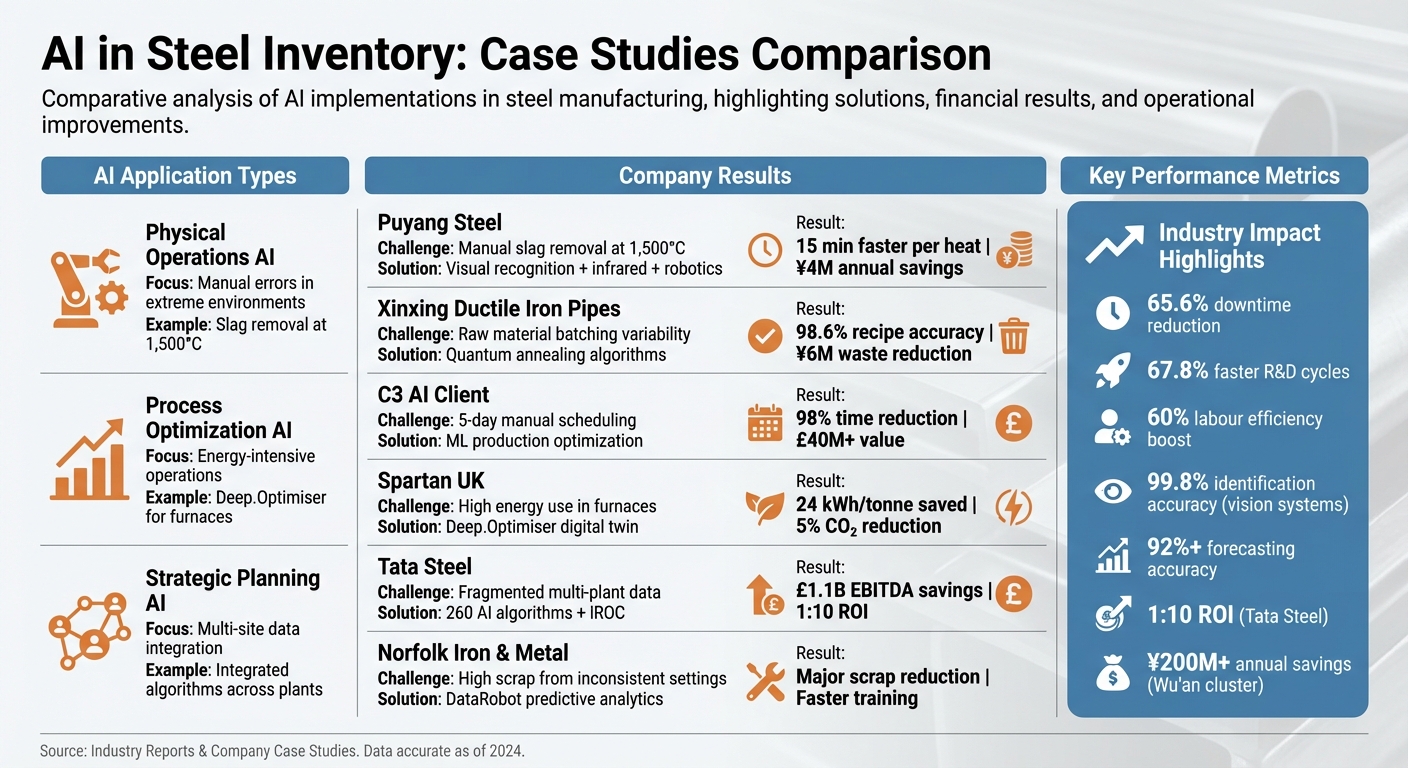
AI Solutions in Steel Manufacturing: Challenges, Solutions, and ROI Comparison
Case studies reveal three distinct ways AI is being applied in steel inventory management:
- Physical operations AI: This approach is used to address manual errors in extreme environments. For instance, twelve Wu’an steel enterprises have implemented AI to optimise slag removal at extreme temperatures of 1,500°C, reducing human error and improving safety [1].
- Process optimisation AI: Spartan UK’s Deep.Optimiser focuses on improving energy-intensive operations, where even small efficiency improvements can lead to substantial cost savings [6].
- Strategic planning AI: Tata Steel utilises integrated algorithms to streamline decision-making and unify data across multiple sites [7].
The financial impact of these AI applications varies widely, depending on the scope of deployment. Tata Steel’s large-scale transformation resulted in £1.1 billion in EBITDA savings, delivering an impressive 1:10 return on investment. In contrast, the Wu’an cluster of steel enterprises reported annual savings exceeding ¥200 million [1][7]. On a smaller scale, Puyang Steel’s AI-driven slag removal system saved ¥4 million annually in alloy costs [1].
When it comes to accuracy, AI systems perform differently based on the task. For example, AI-powered vision systems achieve precision rates as high as 98.7%, while forecasting tools manage over 92% accuracy [1][4]. Physical assessments, like slag removal, tend to hit near-perfect precision, but forecasting tools face challenges due to market volatility and external factors.
Below is a table summarising key challenges, AI solutions, and their outcomes for various companies:
Comparison Table: Challenges, Solutions, and Results
| Company | Primary Challenge | AI Solution Deployed | Measurable Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Puyang Steel | Timing manual slag removal at 1,500°C | Visual recognition with infrared imaging and robotics | Operations 15 minutes faster per heat; ¥4M annual savings [1] |
| Xinxing Ductile Iron Pipes | Variability in raw material batching | Quantum annealing algorithms for recipe optimisation | 98.6% recipe accuracy; ¥6M waste reduction [1] |
| **C3 AI Client** | Manual scheduling taking five days | Machine learning for production schedule optimisation | 98% reduction in planning time; £40M+ economic value [4] |
| Spartan UK | High energy use in reheating furnaces | Deep.Optimiser digital twin platform | 24 kWh/tonne energy saving; 5% CO₂ reduction [6] |
| Tata Steel | Fragmented data across multiple plants | 260 AI algorithms with a remote operations centre | £1.1B EBITDA savings; 1:10 ROI [7] |
| Norfolk Iron & Metal | High scrap rates from inconsistent settings | Predictive analytics via DataRobot | Significant scrap reduction; faster operator training [3] |
The choice of AI solution depends heavily on the specific inefficiencies a manufacturer faces. For instance:
- Companies grappling with safety risks and manual errors might prioritise vision systems and robotics.
- Those focused on cutting energy costs or reducing raw material waste could benefit from process optimisation tools.
- Enterprises with fragmented data and operations across multiple locations may find strategic planning AI indispensable for better forecasting and coordination.
These examples illustrate how tailored AI applications can tackle specific challenges while collectively improving steel inventory management.
Conclusion
AI is reshaping steel inventory management, turning outdated guesswork into precise, data-driven strategies. Across the industry, manufacturers are seeing tangible benefits that directly impact their bottom line.
For instance, AI has been shown to cut downtime by 65.6%, reduce R&D cycle times by 67.8%, and improve labour efficiency by 60% [1]. From optimising energy usage to avoiding costly stockouts, AI addresses inefficiencies that chip away at profitability. As Jayanta Banerjee, Chief Information Officer at Tata Steel, aptly remarked:
Every dollar I spend, I get $10 back [7].
Getting started doesn’t require a monumental leap. Manufacturers can begin with focused pilot projects, invest in reliable data systems, and tackle their most pressing operational challenges. While transitioning from manual processes to automated systems takes time, the 1:10 ROI reported by industry leaders demonstrates that these investments are well worth it [7].
The potential for even greater advancements in metals manufacturing is clear. Tools like GoSmarter are already helping businesses automate inventory management, digitise mill certificates, and simplify compliance processes, making it easier to achieve these efficiencies. The technology is here, and the competitive edge will go to those who act decisively.
FAQs
How does AI enhance accuracy in steel inventory management?
AI brings a new level of precision to inventory management by using computer vision and real-time data integration. It can automatically recognise and monitor steel components, cross-check stock levels with digital records, and flag any inconsistencies on the spot. This minimises human errors and ensures inventory counts are accurate.
By streamlining these tasks, AI not only saves valuable time but also boosts operational efficiency. This gives steel manufacturers tighter control over their inventory, helping to cut down on waste and improve overall stock management.
What financial advantages can AI bring to steel inventory management?
AI-powered inventory management offers impressive financial advantages for steel manufacturers. For example, Wu’an Steel saved over ¥200 million annually, while Tata Steel reported around $1.4 billion in EBITDA savings. Similarly, a global steel producer gained more than $1.7 million in additional profit from just one production line.
By fine-tuning inventory levels, cutting down on waste, and boosting operational efficiency, AI solutions enable businesses to achieve notable cost reductions and improve overall profitability.
How can AI help solve logistical challenges in steel manufacturing?
AI is revolutionising logistics in steel manufacturing by turning scattered and complex data into real-time insights that drive decisions. Take Tata Elxsi, for instance: their AI-powered inventory system gave operators a single, clear view of material levels across multiple service centres. This not only prevented shortages and overstocking but also cut down on unnecessary transport emissions by enabling smarter dispatch planning. In another example, Wu’an Steel managed to slash equipment downtime by 65.6%, saving over £200 million annually and ensuring a smoother flow of materials.
AI also boosts efficiency through predictive analytics, which help forecast demand, optimise stock levels, and fine-tune delivery routes. By analysing past orders, market patterns, and production limitations, AI ensures deliveries are on time while keeping logistics costs in check. Tools like GoSmarter bring these features directly into everyday operations, automating tasks such as tracking inventory, managing orders, and handling compliance paperwork. This allows teams to adapt quickly to changes on the shop floor.
These AI-driven tools not only strengthen supply chain resilience but also cut waste and improve cost management, helping steel manufacturers tackle logistical challenges and operate more efficiently.


